Cheat Sheet
This is a quick “cheat sheet” for myself…
- Separate page for Ubuntu LTS setup…
- Separate page for Windows setup…
- Separate page for Ubuntu LTS setup on Raspberry Pi 5…
- Other stuff as “backups”:
Regular Expressions (Regex)
- inverse match (i.e. match only when substring not found
((?!<substring>).)*
Windows Shell/Command Prompt
- future use
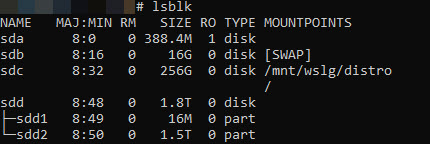
Mounting ext4 Partitions
- advised to use Ext2FSD (updated fork here) unless unable to (e.g. corporate/controlled laptop/desktop)
- in an administrator-level command prompt or PowerShell session:
- list the bare devices
wmic diskdrive list brief
- mount the entire device under WSL
wsl --mount \\.\PHYSICALDRIVEx --bare
- list the bare devices
- in an administrator-level WSL session:
- access the files via Windows Explorer via the “Linux” file storage pass-through
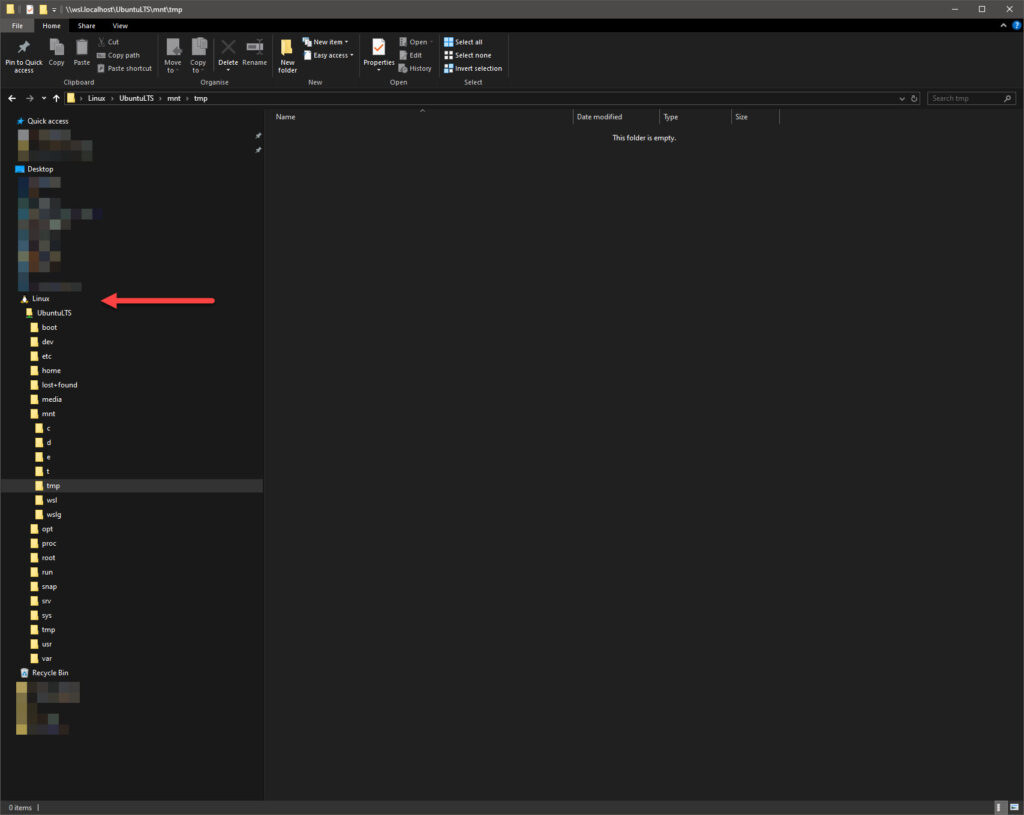
Linux Shell/Command Prompt
- find specifically named files containing a specific string
find . -type f -name "<pattern>" -exec grep -l '<string>' {} \;
- delete all files of a specific name/pattern in current and any sub-directories (without confirmation)
find . -name "<pattern>" -type f -delete
- protect all files of specific names/patterns in current and any sub-directories
find . \( -name "<pattern #1>" -o -name "<pattern #2>" \) -type f -exec chattr +i {} \;
- reboot into UEFI/BIOS from command line
systemctl reboot --firmware-setup
Mounting Devices/Remote Shares
- mount an SMB share
mount -t cifs //<server>/<share> <mount point> -o rw,username='<username>',password='<password>'
- mount an ISO
mount -o loop <ISO path> <mount point>
- mount a partition, assuming supported identifiable format (e.g. FAT32, Ext3/4)
mount /dev/sdxN <mount point>where:- x is the device letter typically starting from ‘a’
- N is the partition number starting from 0
Hard Drive Security
Manipulates drive security as per ATA spec. If drive is external, the USB-to-SATA/PCIe bridge chipset must support/pass-through ATA security commands.
NOTE:
- In odd cases, a secure erase may (re)set the master password as “
NULL” or drive brand (e.g. “SEAGATE” or “ADATA” or “CRUCIAL“). - Read and understand this before attempting anything, particularly when attempting to manipulate master passwords!
- In all the references below,
<user/master flag>is either “u” or “m” denoting user or master password
- unlock a drive
hdparm --user-master <user/master flag> --security-unlock <password> /dev/sdX
- disable security
hdparm --user-master <user/master flag> --security-disable <password> /dev/sdX
- lock a drive
hdparm --user-master <user/master flag> --security-set-passwd <password> /dev/sdX
- secure erase a drive (which usually resets the master password also – see above NOTE)
- WARNING: Irreversible loss of data once command is accepted!
hdparm --user-master <user/master flag> --security-erase <password> /dev/sdXorhdparm --user-master <user/master flag> --security-erase-enhanced <password> /dev/sdX
journalctl
- review system journal in reverse order (earliest entries first)
journalctl -r
- clear journals, leaving only a 1 day’s worth (without changing the configuration permanently)
journalctl --flushjournalctl --rotatejournalctl --vacuum-time=1d
ip
- as the world moves away from the venerable
ifconfig, there is a need to continue to useip:- addresses:
- show IP addresses:
ip address(or simplyip a)
- add IP address:
ip address add <network>/<mask> dev <interface>
- remove IP address:
ip address del <network>/<mask> dev <interface>
- show IP addresses:
- routes:
- show routes:
ip route
- add default route:
ip route add default via <gateway>
- add specific route:
ip route add <network>/<mask> dev <interface>orip route add <network>/<mask> via <gateway>
- save (necessary to commit changes)
ip route save
- show routes:
- links:
- show links:
ip link
- bring link up or down:
ip link set <dev> [up|down]
- show links:
- addresses:
Linux GUI
- to drop to a text console
tty, press the following key combination:CTRL+ALT+F2(i.e.tty2, or otherFncombinations for other terminals) - to get back into the UI, switch back to
tty7by pressing the following key combination:CTRL+ALT+F7
Python
- generate TOTP given seed:
python -c "import pyotp;print(pyotp.TOTP('<seed>').now())"
pyenv
Python version management tends to be a PitA, so here’s some quick cheats:
- install
pyenv:apt install pyenv
- install pyenv-virtualenv:
git clone https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenv.git $(pyenv root)/plugins/pyenv-virtualenv
- list available python versions for
pyenv:pyenv install --list
- install specific python version for
pyenv:pyenv install <version>
- create specific
virtualenvwith specific python version:pyenv virtualenv <version> <venv name>
- show
pyenvversions available:pyenv versions
- set the current directory to use a specific
virtualenv:pyenv local <venv name>
- reset the current directory to use default/system version:
pyenv local system
- set “global” python version:
pyenv global <version>
ffmpeg
- extract specific portions of video w/o re-encoding:
ffmpeg -i <input> -ss <seek timestamp> -t <duration> <output>-ss <seek timestamp>: the timestamp (inh:m:s.ssformat) to start from-t <duration>: the duration of the extracted clip (inh:m:s.ssformat)- note that multiple
-ss <seek timestamp> -t <duration> <output>can be appended to do multiple extractions in one pass
- remove embedded closed captions from video stream (e.g. example
ffprobeoutput below):ffmpeg -i <input> -c copy -bsf:v 'filter_units=remove_types=6' <output>Stream #0:0(und): Video: h264 (High) (avc1 / 0x31637661), yuv420p, 1920x1072 [SAR 1:1 DAR 120:67], Closed Captions, 2150 kb/s, 23.98 fps, 23.98 tbr, 24k tbn, 47.95 tbc (default)Metadata:handler_name : VideoHandlervendor_id : [0][0][0][0]
- removing or re-ordering audio and subtitle tracks:
ffmpeg -i <input> -map 0:v:0 -map 0:a:<index> -map 0:s:<index> -c copy <output>(assuming only single input and single video stream, all<source>entries for the-map <source>:<type>:<index>parameters is always0)-map 0:a:<index>: zero-based index of the audio track (i.e. even if multiple audio streams exist, and/or the first audio track isstream#0:n, the first audio track’s index is still “0“); multiple entries can be used, with the new order based on the order the -map parameter appears-map 0:s:<index>: zero-based index of the subtitle track (i.e.even if multiple subtitle streams exist, and/or the first subtitle track isstream#0:n, the first audio track’s index is still “0“); multiple entries can be used, with the new order based on the order the-mapparameter appears- any unmapped streams will be omitted in the output (i.e. if you left out the
-map 0:v:0, there will be no video stream)
- removing or switching default audio and subtitle tracks:
ffmpeg -i <input> -c copy <output> -dispositions:<type>:<index> 0 -dispositions:<type>:<index> default <output>-dispositions:<type>:<index> 0: remove stream<index>as the default stream for<type>-dispositions:<type>:<index> default: set stream<index>as the default stream for<type>- note that the
<index>is based on the output streams order (e.g. if placed after other-mapparameters)
- merging a single separate audio and video stream:
ffmpeg -i <audio stream input> -i <video stream input> -c copy <output>- note that this assumes both streams have the same duration, and each input file only has one audio and video stream; if there are more, or if there are other streams (e.g. subtitles), these will all be merged – if only specific streams are required, use the
-mapparameters
- note that this assumes both streams have the same duration, and each input file only has one audio and video stream; if there are more, or if there are other streams (e.g. subtitles), these will all be merged – if only specific streams are required, use the
- changing/deleting the metadata on entire file and individual streams:
ffmpeg -i <input> -metadata <tag>="<value>" -metadata <tag>=""-map 0:v:0 -metadata:s:v:0 <tag>="<value>" -map 0:a:0 -metadata:s:a:0 <tag>="<value>" -map 0:s:0 -c copy <output>- note that in the above example format, only the main metadata, video and audio streams “
0” require metadata changes/deletions, i.e. any-metadataparameters apply only to the preceding-mapand if placed before any-map, applies to the main metadata
- note that in the above example format, only the main metadata, video and audio streams “
OpenSSL
- encode a string using AES and a password:
echo -n "<string>" | openssl enc -e -pbkdf2 -aes-256-cbc -a -nosalt
- decode an AES-encoded string (from above) using a password:
echo -n "<encryptedstring>" | openssl enc -d -pbkdf2 -aes-256-cbc -a -nosalt
SSL/TLS Certificates and Server Connections
The following section/s shows some commands to obtain the data as per section heading.
- grabbing certificate chain
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect <server:port>
- testing TLS version
openssl s_client -connect <server:port> [ -tls1 | -tls1_1 | -tls1_2 | -tls1_3 ]- empty result likely shows the server does not support said TLS version, example:
% openssl s_client -connect localhost:443 -tls1_3 CONNECTED(00000003) closed --- no peer certificate available --- No client certificate CA names sent --- SSL handshake has read 7 bytes and written 241 bytes Verification: OK --- New, (NONE), Cipher is (NONE) Secure Renegotiation IS NOT supported Compression: NONE Expansion: NONE No ALPN negotiated Early data was not sent Verify return code: 0 (ok) ---
- testing accepted ciphers
nmap -script ssl-enum-ciphers -p <port> <server>
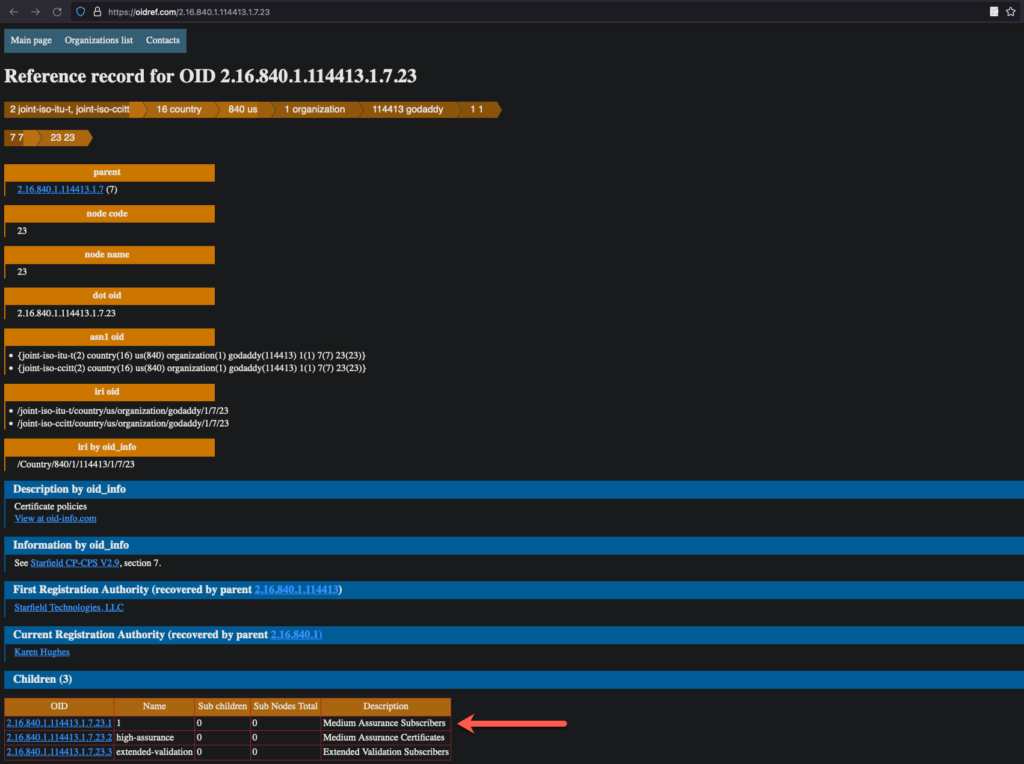
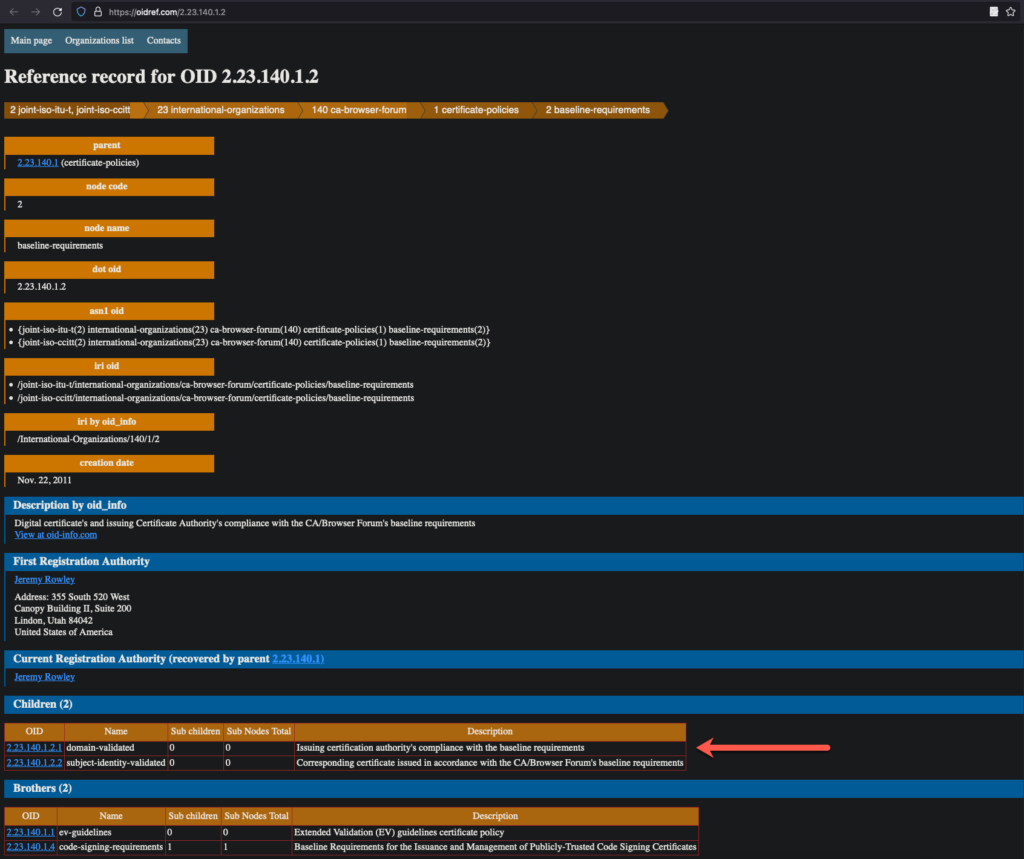
- testing for EV (Extended Validation) certificates
- run the following command to retrieve the OIDs from the
Policy:echo | openssl s_client -connect www.globalsign.com:443 2>&1 | openssl x509 -noout -ext certificatePolicies
- subsequently, taking the
OID, check with either:http://oid-info.com/get/<OID>orhttps://oidref.com/<OID less last decimal/leaf node>
- examples:
- screenshot from https://oidref.com/2.16.840.1.114413.1.7.23
- screenshot from https://oidref.com/2.23.140.1.2
- screenshot from https://oidref.com/2.16.840.1.114413.1.7.23
- run the following command to retrieve the OIDs from the